leeb rebound hardness test principle|equotip hardness : traders Depending on the probe (“impact device”) and indenter (“impact body”) types that vary by geometry, size, weight, material and spring force, . See more
STATIM G4 Cassette Autoclaves provide sterilization and dryness at speeds faster than conventional chambered autoclaves, and automatically record & monitor cyclesWhen comparing these sterilizing options, both Statim, and traditional autoclaves like Midmark, perform sufficient results. Each perform at a reasonable time frame, however the Statim beats cycle time in regards to un .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Standard Operating Procedure should be present near the autoclave unit for reference. Supervisors are responsible for ensuring that employees are properly trained before operating .
The Leeb Rebound Hardness Test (LRHT) invented by Swiss company Proceq SA is one of the four most used methods for testing metal hardness. This portable method is mainly used for testing sufficiently large workpieces (mainly above 1 kg). It measures the coefficient of restitution. It is a form of . See more
The Equotip (later on also called simultaneously as Leeb method) rebound hardness test method was developed in the year 1975 by Leeb and Brandestini at Proceq SA to . See more
• German standards and specifications:• American standards:• Official international standards projects:• Official . See more• http://grhardnesstester.com/blog/methods-testing-hardness-steel/• https://www.baq.de/template.cgi?page=service_infos_ueber_messverfahren&rubrik=&id=&lang.The traditional methods are based on well-defined physical indentation hardness tests. Very hard indenters of defined geometries and sizes . See more
Depending on the probe (“impact device”) and indenter (“impact body”) types that vary by geometry, size, weight, material and spring force, . See more• Meyer hardness test See more Using an ultrasonic hardness tester, the Leeb Rebound tester can inspect the parts below 2mm (0.11″) supported or combined with a heavier .Another well-known principle for portable hardness testers is the rebound method. The DynaMIC and DynaPOCKET (Krautkramer), for example, measure the velocity of a propelled impact .
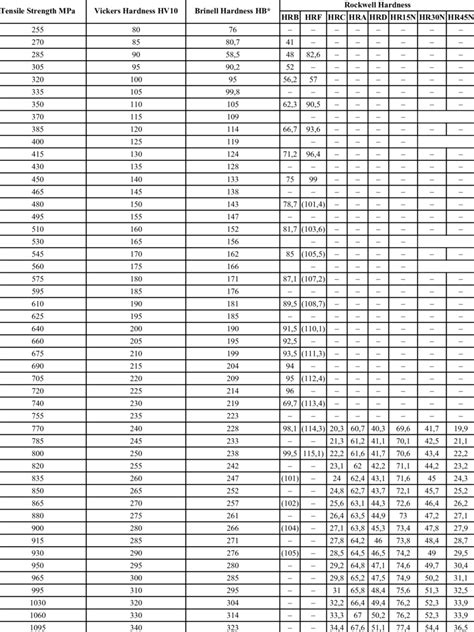
leebs hardness chart
The core principle of the Leeb method revolves around measuring energy loss. During the test, an impact body strikes the metallic surface. The resulting loss of energy due to material deformation is meticulously measured, . The Leeb hardness test is of the dynamic or rebound type, which primarily depends both on the plastic and on the elastic properties of the material being tested. The .Determination of the hardness of metallic materials according to Leeb is defined in the ISO 16859 and ASTM A956 standards. In this dynamic test method, the ratio of rebound velocity to impact velocity of a moving impactor is used to .
leeb rebound hardness test wikipedia
The Leeb hardness test (LHT with test value of L D ) is a rebound hardness test, originally developed for metals, that has been correlated with the Unconfined Compressive . The Leeb hardness number (L) is calculated from the ratio of the rebound velocity to the impact velocity of a spherically shaped tungsten carbide, silicon nitride, or diamond .
The Leeb Rebound Hardness Test (LRHT) invented by Swiss company Proceq SA is one of the four most used methods for testing metal hardness. This portable method is mainly used for .Using an ultrasonic hardness tester, the Leeb Rebound tester can inspect the parts below 2mm (0.11″) supported or combined with a heavier part or up to any thickness; Measure the .
The Leeb method principle uses a spherical tungsten carbide ball and a spring load to measure the hardness of a test piece. This method uses a rebound technique which measures the .Another well-known principle for portable hardness testers is the rebound method. The DynaMIC and DynaPOCKET (Krautkramer), for example, measure the velocity of a propelled impact . The core principle of the Leeb method revolves around measuring energy loss. During the test, an impact body strikes the metallic surface. The resulting loss of energy due to .
The Leeb hardness test is of the dynamic or rebound type, which primarily depends both on the plastic and on the elastic properties of the material being tested. The .Determination of the hardness of metallic materials according to Leeb is defined in the ISO 16859 and ASTM A956 standards. In this dynamic test method, the ratio of rebound velocity to . The Leeb hardness test (LHT with test value of L D ) is a rebound hardness test, originally developed for metals, that has been correlated with the Unconfined Compressive .
The Leeb hardness number (L) is calculated from the ratio of the rebound velocity to the impact velocity of a spherically shaped tungsten carbide, silicon nitride, or diamond .Principle. The Leeb hardness test defines the hardness HL as the quotient of the velocities before and after the impact of a well-defined impact body (mostly with a spherical contact area) and a .The Leeb Rebound Hardness Test (LRHT) invented by Swiss company Proceq SA is one of the four most used methods for testing metal hardness. This portable method is mainly used for .
iss pipette calibration
Using an ultrasonic hardness tester, the Leeb Rebound tester can inspect the parts below 2mm (0.11″) supported or combined with a heavier part or up to any thickness; Measure the .
The Leeb method principle uses a spherical tungsten carbide ball and a spring load to measure the hardness of a test piece. This method uses a rebound technique which measures the .Another well-known principle for portable hardness testers is the rebound method. The DynaMIC and DynaPOCKET (Krautkramer), for example, measure the velocity of a propelled impact . The core principle of the Leeb method revolves around measuring energy loss. During the test, an impact body strikes the metallic surface. The resulting loss of energy due to .
The Leeb hardness test is of the dynamic or rebound type, which primarily depends both on the plastic and on the elastic properties of the material being tested. The .
Determination of the hardness of metallic materials according to Leeb is defined in the ISO 16859 and ASTM A956 standards. In this dynamic test method, the ratio of rebound velocity to . The Leeb hardness test (LHT with test value of L D ) is a rebound hardness test, originally developed for metals, that has been correlated with the Unconfined Compressive .
The Leeb hardness number (L) is calculated from the ratio of the rebound velocity to the impact velocity of a spherically shaped tungsten carbide, silicon nitride, or diamond .
leeb hardness tester principle
Batch retorts are the most predominant type of in-container, thermal sterilization systems used by food and beverage processors throughout the world today. Batch retorts are, just as the name implies, sterilization .
leeb rebound hardness test principle|equotip hardness